There are some hopes that the sun will become a main source of energy in
the 21st century. By then, sources of oil will be almost exhausted and
will only play a minor part in the supplying of energy. Interested to know how to make a simple solar tracker with dual axis? Learn More
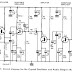
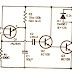
The present interest in solar energy is therefore not surprising. Some work has already been done with solar cells and solar panels. However, these only operate with optimum performance when positioned exactly at right- angles to the sun. Unfortunately, this situation is not usual in our latitudes unless the solar panels are rotated with respect to the sun. The efficiency of a solar panel system can be improved if the panels track the sun, and remain as long as possible at the most favorable angle of incidence. The circuitry required is relatively simple. lt uses a window comparator which keeps the drive motor idle, as long as the two LDrs are subjected to the same illumination. Half the operating voltage is then applied to the non-inverting input of A1 and to the inverting input of A2. When the position of the sun changes, the illumination affecting LDRs R1 and 1 R2 is different, if they are at an angle to each other as shown in figure 2. In this case, the input voltage for the window comparator deviates from half the supply voltage, so that the output of the comparator provides information to the motor for clockwise or anticlockwise rotation. Transistors T1 . . . T4 in a bridge circuit cater for reversing of I the motor. Diodes D1 . . . D4 serve I to suppress voltage peaks which can 1 be produced when the motor is switched. Preset potentiometers P1 and P2 are used for alignment. They are adjusted so that the motor is idle when the LDRs are subjected to the same illumination. if less light reaches LDR R2 than LDR R1 , the voltage at point A rises to more than half the supply voltage. The result is that the output of A1 goes high and transistors T1 and T4 conduct. The motor then runs. if the illumination of the LDRs is then changed so that the voltage at point A drops to less than half the supply voltage, output A2 goes high T and transistors T3 and T2 must conduct. The motor them rotates in the opposite direction. Small geared motors of the type used for models, with a suitable voltage and maximum operating current of 300 mA, are suitable for driving the solar panels. The use of this control circuit makes it possible to control the solar panel in one plane. Of course, in order to track the sun from sunrise to sun- down, two control circuits will be required: one for horizontal and one for vertical tracking.
The present interest in solar energy is therefore not surprising. Some work has already been done with solar cells and solar panels. However, these only operate with optimum performance when positioned exactly at right- angles to the sun. Unfortunately, this situation is not usual in our latitudes unless the solar panels are rotated with respect to the sun. The efficiency of a solar panel system can be improved if the panels track the sun, and remain as long as possible at the most favorable angle of incidence. The circuitry required is relatively simple. lt uses a window comparator which keeps the drive motor idle, as long as the two LDrs are subjected to the same illumination. Half the operating voltage is then applied to the non-inverting input of A1 and to the inverting input of A2. When the position of the sun changes, the illumination affecting LDRs R1 and 1 R2 is different, if they are at an angle to each other as shown in figure 2. In this case, the input voltage for the window comparator deviates from half the supply voltage, so that the output of the comparator provides information to the motor for clockwise or anticlockwise rotation. Transistors T1 . . . T4 in a bridge circuit cater for reversing of I the motor. Diodes D1 . . . D4 serve I to suppress voltage peaks which can 1 be produced when the motor is switched. Preset potentiometers P1 and P2 are used for alignment. They are adjusted so that the motor is idle when the LDRs are subjected to the same illumination. if less light reaches LDR R2 than LDR R1 , the voltage at point A rises to more than half the supply voltage. The result is that the output of A1 goes high and transistors T1 and T4 conduct. The motor then runs. if the illumination of the LDRs is then changed so that the voltage at point A drops to less than half the supply voltage, output A2 goes high T and transistors T3 and T2 must conduct. The motor them rotates in the opposite direction. Small geared motors of the type used for models, with a suitable voltage and maximum operating current of 300 mA, are suitable for driving the solar panels. The use of this control circuit makes it possible to control the solar panel in one plane. Of course, in order to track the sun from sunrise to sun- down, two control circuits will be required: one for horizontal and one for vertical tracking.
Making a dual axis solar tracker circuit mechanism:



No comments:
Post a Comment